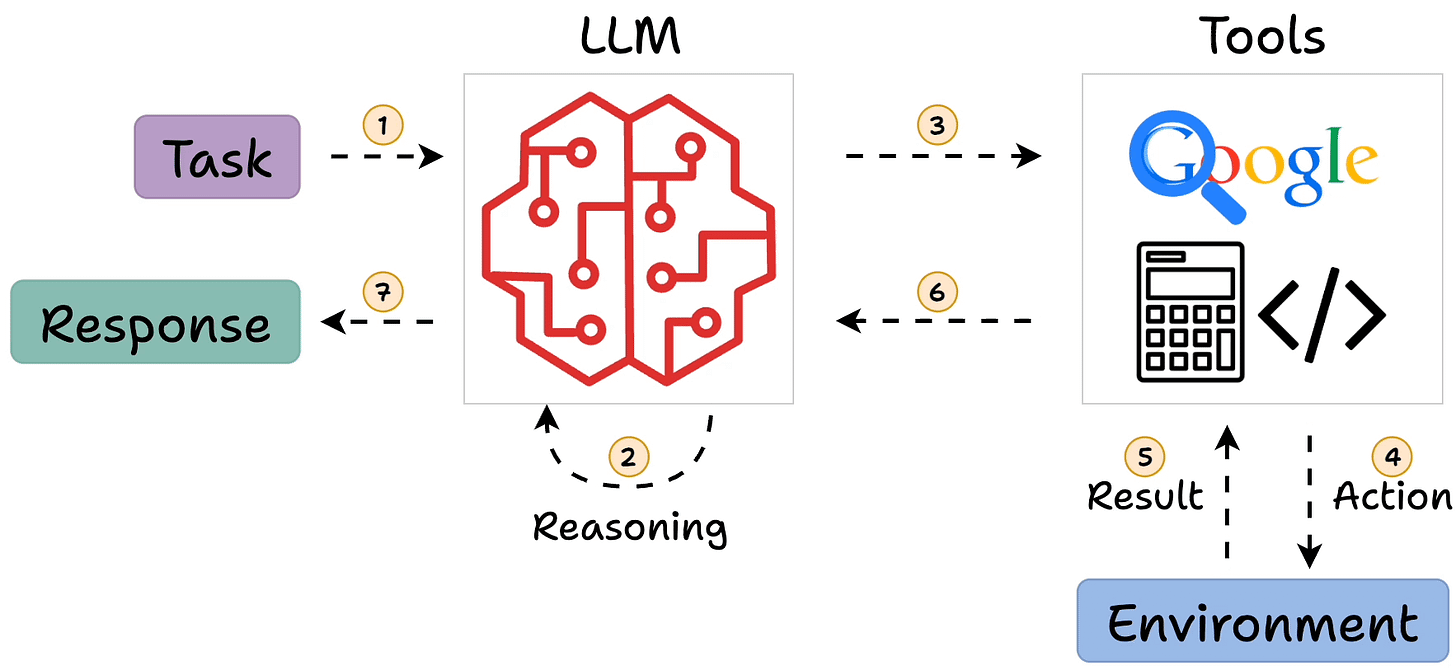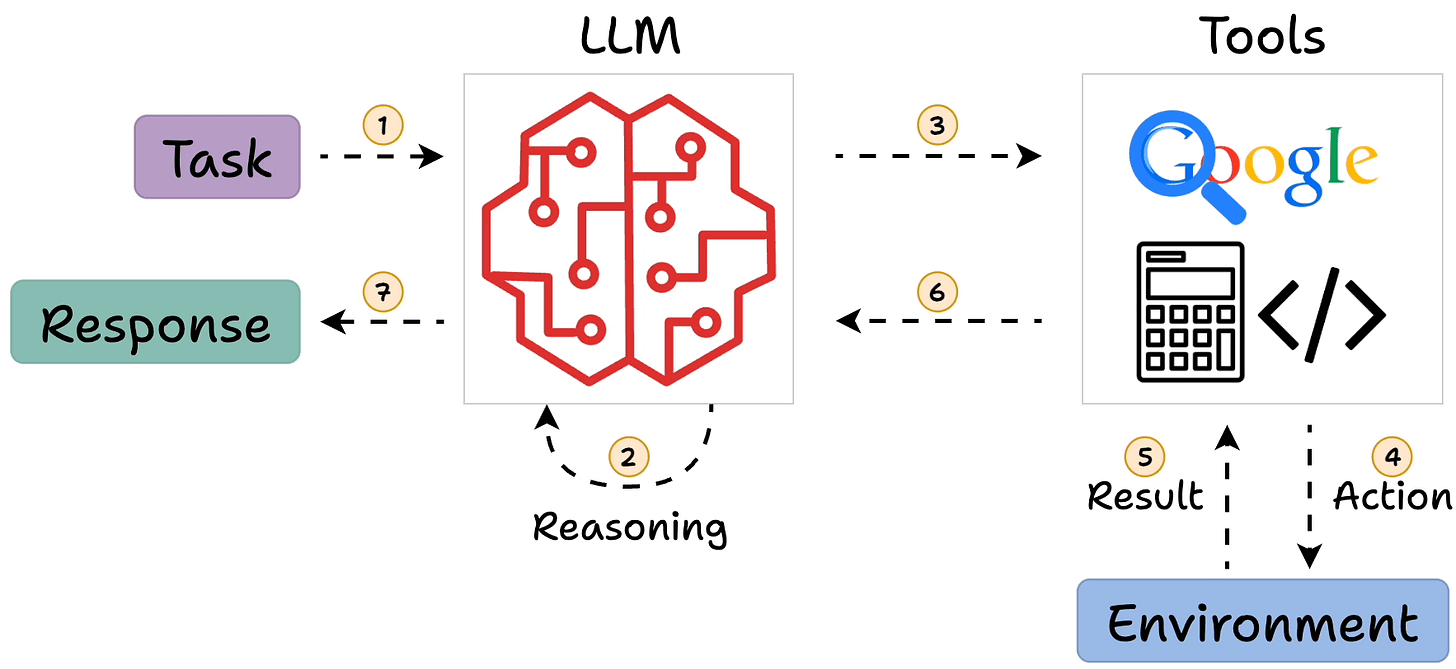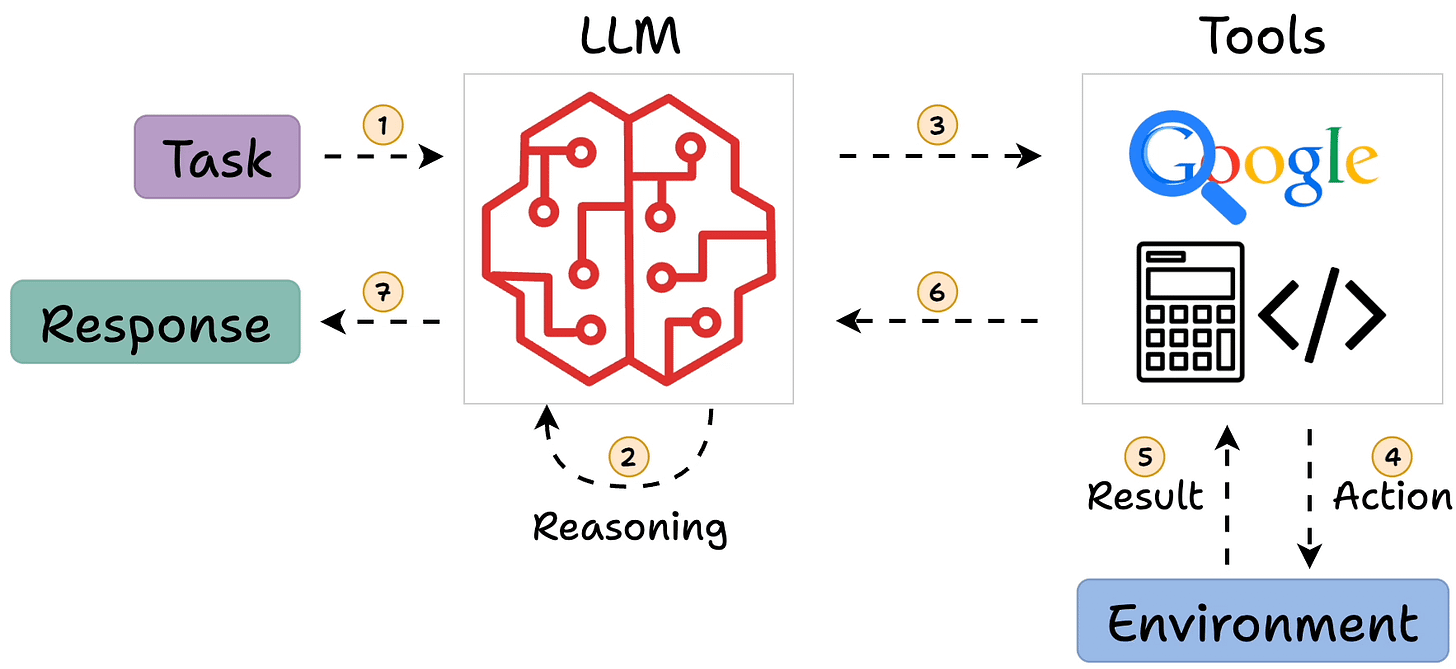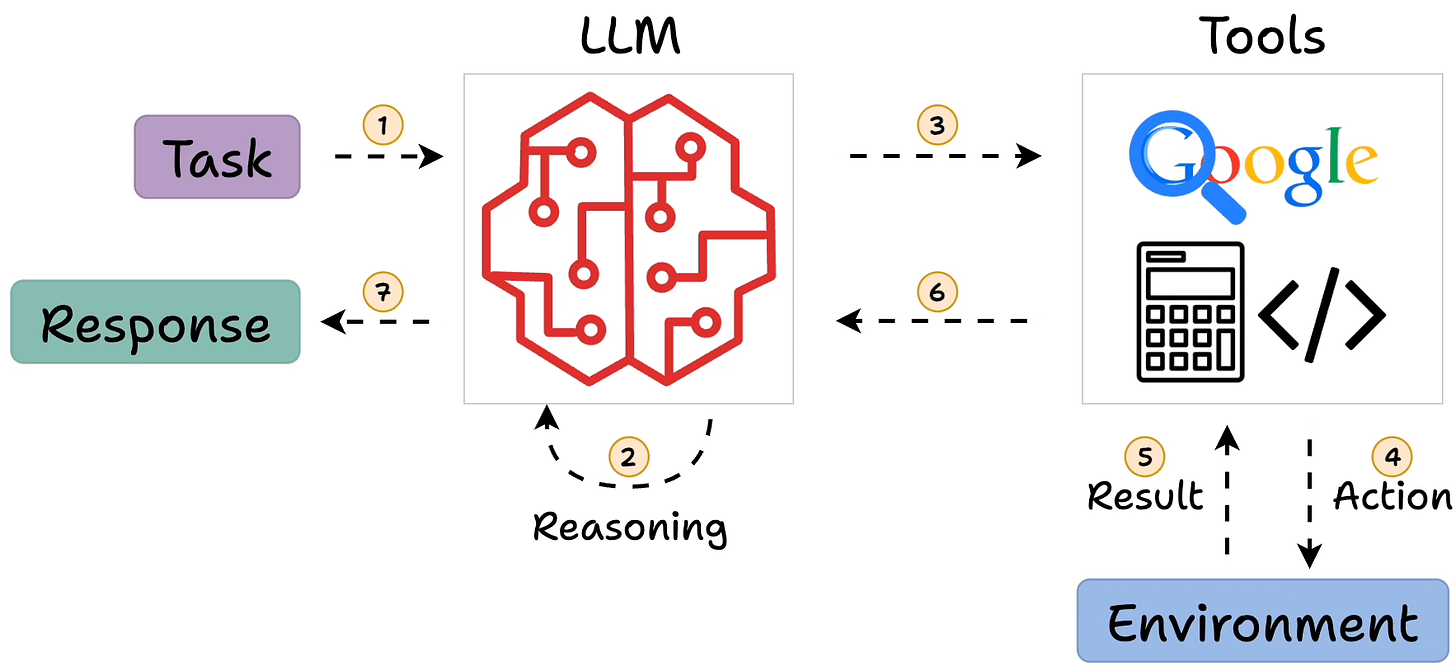
This repository implements a simple Python-based ReAct (Reason + Act) model for Large Language Models (LLMs). The goal is to extend the capabilities of LLMs by allowing them to access external tools, perform API calls, and execute code. This setup breaks free from the initial environment constraints and enables LLMs to interact with the world outside the original prompt.
The ReAct model is described in the ReAct Paper, which outlines how a language model can be enhanced by enabling it to reason and perform actions. Actions such as web searching, calculations, and more are integrated into the LLM's reasoning cycle.
This notebook leverages the Gemini chat completion API to implement the ReAct framework, enabling advanced reasoning and interaction with external tools.
The notebook provides a set of simple actions that the model can perform, including:
- Wikipedia Search (
wikipedia: <search term>): Searches Wikipedia and returns the summary of the first result. - Calculate (
calculate: <expression>): Evaluates a mathematical expression using Python'seval()function (note: be cautious when usingeval()with untrusted input). - Advanced Search (
search_advanced: <search term>): Performs a Google search using the Tavily API.
These actions are designed to help the model access external data sources, perform calculations, and interact with the environment, making it more dynamic and capable of handling diverse queries.
-
wikipedia:
wikipedia: Django
Retrieves a summary of the Wikipedia page for "Django." -
calculate:
calculate: 4 * 7 / 3
Performs the calculation and returns the result. -
search_advanced:
search_advanced: New news update about Messi
Searches the web for news about Lionel Messi and returns a summary.
- Python 3.8+
- Install the necessary Python packages:
pip install openai httpx tavily
- Google API Key: If using the Gemini model, set the environment variable
GOOGLE_API_KEYto your API key. - Model Configuration: By default, the code uses the Gemini API for the model (
gemini-2.0-flash). If you'd prefer to use OpenAI, modify theBASE_URLandMODELvalues accordingly.
API_KEY = os.getenv("GOOGLE_API_KEY") # Replace with OpenAI_API_KEY if using OpenAI
BASE_URL = "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/openai/" # Set to None if using OpenAI
MODEL = "gemini-2.0-flash" # Replace with your OpenAI model nameTo start querying the model, use the query() function:
question = "What is the capital of France?"
query(question)The model will reason about the question, select the appropriate action, perform it, and output the results.
The available actions are implemented as functions that the model can invoke:
- wikipedia(q): Retrieves a summary from Wikipedia in both English and Vietnamese.
- calculate(what): Evaluates a Python expression.
- search_advanced(query): Performs a web search using the Tavily API and returns the top result.
These actions are executed by the ChatBot_ReAct class, which maintains the conversation context and orchestrates the reasoning process.
- User Input: "What is the capital of France?"
- Thought: "I should look up France on Wikipedia."
- Action:
wikipedia: France - Observation: "France is a country. The capital is Paris."
- Final Answer: "The capital of France is Paris."
- The
eval()function used in thecalculateaction can be dangerous if used with untrusted input, so be cautious when handling input from users. - The
search_advancedfunction uses the Tavily API to perform web searches. You may want to adjust the search query or results handling as needed. - The
base_urlparameter can be modified to use OpenAI's models instead of the Gemini API. Check the comments in the code for how to make this switch.
Kho lưu trữ này triển khai một mô hình ReAct (Reason + Act) dựa trên Python cho Mô hình Ngôn ngữ Lớn (LLMs). Mục tiêu là mở rộng khả năng của LLMs bằng cách cho phép chúng truy cập các công cụ bên ngoài, thực hiện các cuộc gọi API và chạy mã. Cấu hình này giúp phá vỡ các ràng buộc của môi trường ban đầu và cho phép LLM tương tác với thế giới bên ngoài.
Mô hình ReAct được mô tả trong ReAct Paper, trong đó giải thích cách mà một mô hình ngôn ngữ có thể được nâng cao bằng cách cho phép nó lý luận và thực hiện các hành động. Các hành động như tìm kiếm web, tính toán và nhiều hơn nữa đã được tích hợp vào chu trình lý luận của LLM.
Notebook này sử dụng Gemini chat completion API để triển khai mô hình ReAct, giúp lý luận và tương tác với các công cụ bên ngoài một cách mạnh mẽ.
Notebook cung cấp một bộ hành động đơn giản mà mô hình có thể thực hiện, bao gồm:
- Tìm kiếm Wikipedia (
wikipedia: <từ khóa tìm kiếm>): Tìm kiếm trên Wikipedia và trả về đoạn trích từ kết quả đầu tiên. - Tính toán (
calculate: <biểu thức>): Đánh giá biểu thức toán học sử dụng hàmeval()của Python (lưu ý: hãy cẩn thận khi sử dụngeval()với đầu vào không đáng tin cậy). - Tìm kiếm nâng cao (
search_advanced: <từ khóa tìm kiếm>): Thực hiện tìm kiếm trên Google sử dụng API Tavily.
Các hành động này giúp mô hình truy cập nguồn dữ liệu bên ngoài, thực hiện tính toán và tương tác với môi trường, làm cho mô hình trở nên năng động và có khả năng xử lý các câu hỏi đa dạng.
-
wikipedia:
wikipedia: Django
Tìm kiếm và lấy đoạn trích của trang Wikipedia "Django." -
calculate:
calculate: 4 * 7 / 3
Thực hiện phép tính và trả về kết quả. -
search_advanced:
search_advanced: New news update about Messi
Tìm kiếm trên web về tin tức liên quan đến Lionel Messi và trả về kết quả tóm tắt.
- Python 3.8+
- Cài đặt các gói Python cần thiết:
pip install openai httpx tavily
- Khóa API Google: Nếu sử dụng mô hình Gemini, thiết lập biến môi trường
GOOGLE_API_KEYvới khóa API của bạn. - Cấu hình mô hình: Mặc định, mã sử dụng API Gemini cho mô hình (
gemini-2.0-flash). Nếu bạn muốn sử dụng OpenAI, hãy sửa đổi giá trịBASE_URLvàMODELcho phù hợp.
API_KEY = os.getenv("GOOGLE_API_KEY") # Thay bằng OPENAI_API_KEY nếu dùng OpenAI
BASE_URL = "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/openai/" # Đặt None hoặc không truyền tham số này nếu dùng OpenAI
MODEL = "gemini-2.0-flash" # Thay bằng tên mô hình OpenAI của bạnĐể bắt đầu truy vấn mô hình, sử dụng hàm query():
question = "What is the capital of France?"
query(question)Mô hình sẽ lý luận về câu hỏi, chọn hành động phù hợp, thực hiện hành động và đưa ra kết quả.
Các hành động có sẵn được triển khai dưới dạng các hàm mà mô hình có thể gọi:
- wikipedia(q): Lấy đoạn trích từ Wikipedia bằng tiếng Anh và tiếng Việt.
- calculate(what): Đánh giá biểu thức toán học bằng Python.
- search_advanced(query): Thực hiện tìm kiếm web sử dụng API Tavily và trả về kết quả đầu tiên.
Các hành động này được thực thi bởi lớp ChatBot_ReAct, lớp này duy trì bối cảnh cuộc trò chuyện và điều phối quá trình lý luận.
- Người dùng nhập: "What is the capital of France?"
- Suy nghĩ: "Tôi nên tìm kiếm về Pháp trên Wikipedia."
- Hành động:
wikipedia: France - Quan sát: "Pháp là một quốc gia. Thủ đô là Paris."
- Câu trả lời cuối cùng: "Thủ đô của Pháp là Paris."
- Hàm
eval()được sử dụng trong hành độngcalculatecó thể nguy hiểm nếu sử dụng với đầu vào không đáng tin cậy. Hãy cẩn thận khi xử lý đầu vào từ người dùng. - Hàm
search_advancedsử dụng API Tavily để tìm kiếm trên web. Bạn có thể điều chỉnh truy vấn tìm kiếm hoặc cách xử lý kết quả nếu cần. - Tham số
base_urlcó thể được thay đổi để sử dụng mô hình của OpenAI thay vì Gemini API. Xem chú thích trong mã để biết cách thực hiện thay đổi này.